In the transport, shipping, and logistics (TSL) industry, key priorities include fast information processing, error reduction, and seamless coordination of multiple dispersed activities—from cargo booking by a freight forwarder to real-time fleet updates. The use of mapping and cloud technologies in Gamuza paves the way for easily transferring similar solutions to transport and logistics.
Managing vegetation in power line corridors might seem far removed from the daily reality of the TSL sector. Yet, the implementation of the Gamuza system by software firm IT-solve demonstrates that advanced GIS mapping technologies, database integrations, and process automation can be successfully applied to other domains—from vehicle route optimization to document management and field coordination.
Gamuza proves that innovations in mapping, cloud computing, and process automation can significantly boost the efficiency of any organization—including those in the TSL industry. Better operational control and smoother information flow can directly impact profits, safety, and stakeholder satisfaction.
The Challenge: Streamlining Field Processes
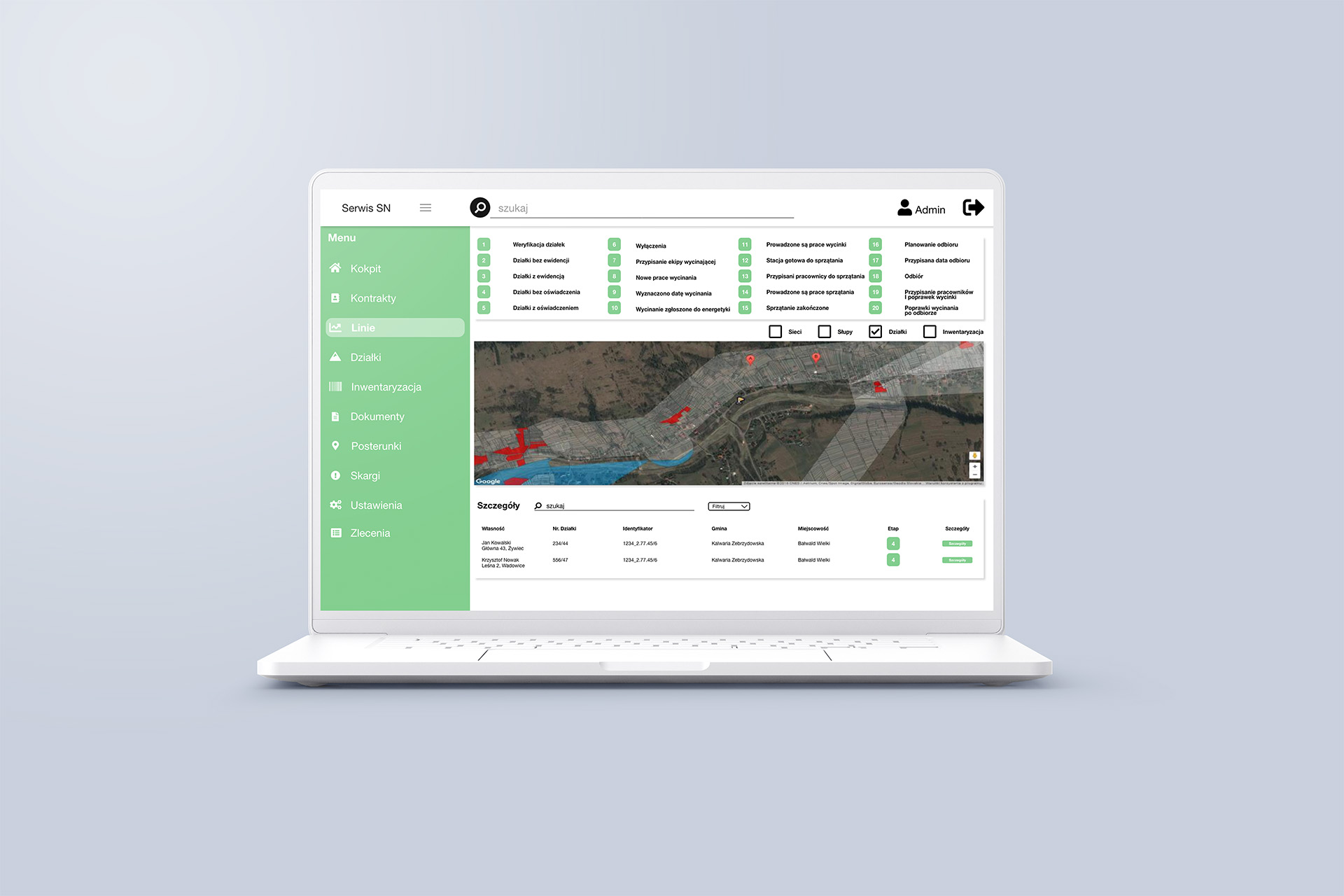
Before the integrated solution was implemented, Gamuza’s field technicians had to manually record the coordinates of trees for removal and search for parcel owner information themselves. In the context of power lines, this created a high risk of errors and delays, as every inconsistency or lack of updates could result in administrative issues and additional costs.
In the TSL sector, similar manual and fragmented workflows still occur surprisingly often. This applies to transport planning, compiling shipment documents, or filling out route cards. In all these cases, the lack of automation causes the same problems: bureaucracy, high servicing costs, and inconsistent data.
A Comprehensive Solution for Gamuza
Collaboration with IT-SOLVE led to the development of a solution that eliminated coordination problems and time-consuming administrative processes. At the heart of the project was the integration of Gamuza with mapping tools (Quantum GIS, Geoportal). In practice, this means quickly identifying parcel locations, automatically obtaining ownership data, and efficiently tracking the entire vegetation management process.
From a logistics CTO’s perspective, this presents a blueprint for similar deployments—whether for supply chain management or advanced infrastructure mapping in road or rail transport.
Key Technologies Used
Gamuza leverages a tech stack that is equally well-suited for scalable TSL applications:
- ASP.NET MVC – A stable backend environment for building complex applications handling multiple business processes.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Azure – Cloud platforms offering high performance and availability, crucial for large-scale field operations and uninterrupted data access.
- QGIS (formerly Quantum GIS) – Advanced GIS software for visualizing, editing, analyzing, and publishing geospatial data. In logistics, it supports network analysis, spatially-informed supply chain management, real-time fleet monitoring, cost analysis by region, and planning multimodal transport connections. It allows multilayer mapping, data integration from multiple sources, and spatial analyses supporting decision-making throughout the supply chain.
- Bootstrap – Enables responsive UI design, ideal for mobile apps used by drivers or dispatchers.
- PostgreSQL – A powerful database that efficiently manages large volumes of spatial data.
This architecture allowed Gamuza to scale the system, continuously update it, and securely store data. A similar technological foundation could prove equally beneficial for handling less-than-truckload (LTL) shipments or international logistics projects.
Results of the Gamuza Implementation
- Administrative Automation
The solution significantly shortened bureaucratic workflows and document exchange. In TSL, this would mean less paperwork and faster confirmation of transport orders. - Improved Field Coordination
Integration with mapping databases gives field employees real-time access to accurate data. Similarly, dispatchers in logistics could dynamically plan and adjust driver routes. - Precise Work Planning
Quantum GIS enables pinpointing exactly where further actions are needed (e.g., tree felling or inspection). In TSL, similar logic could be applied to route optimization or monitoring key transshipment points. - Flexibility and Scalability
Technologies like AWS and Azure handle varying workloads very well. This is essential in the TSL sector, where traffic intensity and demand fluctuate.
How Gamuza Inspires the TSL Sector
Although Gamuza operates in the energy sector, specifically vegetation management under high-voltage lines, it proves that a well-designed GIS-based system with thoughtful process automation can solve similar challenges in other industries. For TSL, where real-time information, error reduction, and coordination of dispersed operations are crucial, such a solution offers immediate value.
The use of mapping and cloud technologies in Gamuza demonstrates a clear opportunity for the TSL industry to:
- Improve route planning,
- Gain better supply chain visibility,
- Streamline document handling.
In essence, Gamuza offers a scalable, modular model for innovation that TSL leaders can adapt to meet the growing complexity of today’s transportation networks.